There are few things more frustrating than loving an anime that has room to grow as a story, but never gets beyond one season of material. It’s arguably even more of an irritance when you know the second season would easily pay for itself. Fortunately, it’s very rare for popular anime to not get sequels (happens only about 20% of the time), and there are ways to predict which ones those will be. I like to think knowing softens the heartbreak.
Tag Archives: Fun With Numbers
Fun With Numbers: Explaining Yozakura Quartet’s Second Season
A little over a week ago, I wrote about how seemingly improbable this season’s Yozakura Quartet sequel was. It was anomaly, lacking any of the traditional indicators (profitable disc sales, TV ratings in excess of 3%, visible boost in the sales totals of the manga). Or at least it was until you look at the unique way in which the most recent series of OADs was marketed. As it turns out, the Yozakura Quartet OADs, though failing to chart, were very probably profitable. The makers made their dues by exploiting a bit of a backdoor in the niche anime industry: piggybacking on the much larger manga market.
Fun With Numbers: The Anime Industry Is Demonstrably Healthy (And Not Dying)
Much has often been made of how the anime industry has evolved over the years. Whenever this is pointed out, it’s usually framed in the form of some criticism; the prevailing artstyle has changed (somewhat true, but largely irrelevant), the amount of ecchi/harem anime has increased (true, though they are now less profitable than other genres), awesome manly anime don’t get made like they used to be (false), artsy anime never sell these days (false). One of the bigger indicators of sour grapes on the part of people offering such criticisms is the assertion that it wasn’t always this way, that whatever change they point out in modern anime is a symptom of the declining health of a sickly industry doomed to implode upon itself.* In reality, that implosion kind of already happened back in 2007; anime makers overproduced and had a bad year, and so made an industry-wide decision to cut back on the number of anime being made yearly. The result? Anime’s still here; the worst that happened was that 2010-2011 saw production drop back to 2003 levels, and 2012 saw an increase in production equivalent to the 2009-2010 dropoff:
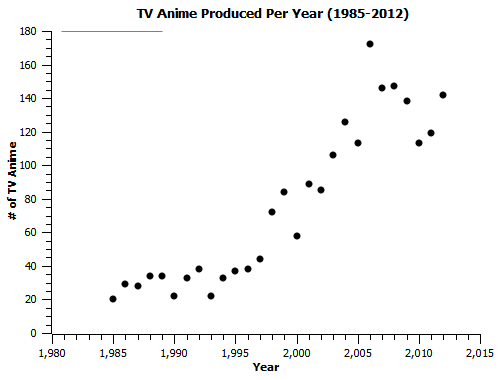 Just because the industry’s making lots of stuff doesn’t mean it’s all selling well, though. That’s another point worth examining, because it turns out anime nowadays is better at churning out hits than it’s been at any point in the past.
Just because the industry’s making lots of stuff doesn’t mean it’s all selling well, though. That’s another point worth examining, because it turns out anime nowadays is better at churning out hits than it’s been at any point in the past.
Fun With Numbers: Yozakura Quartet Gets a Sequel for No Apparent Financial Reason
I’m pretty ok with Yozakura Quartet getting its second crack at TV anime this season. It’s a series with a lot of potential; if nothing else, the power to produce machine guns out of thin air that fire when you say bang-bang is a unique one. But the manga is a repetitive criminally slow-paced monthly, the first anime was a hopelessly melodramatic show that failed to top 1000 in average volume sales, and the second, OVA-based anime was a thinly-veiled sakuga showcase. It’s a series that definitely could get over the hump, and clearly people care enough to keep trying.
But why? I’ve got no financial explanation. Given that its season 1 sales were less than borderline and the OVA failed to chart, the fact that it’s still getting anime is impressive and puts it in a very small circle. It’s not that the new series has been promoting the manga like a Blue Exorcist or an Inu x Boku SS either; the 7th volume in 2009 and the 13th volume in 2013 logged near-identical 70,000 volume sales totals. The most popular installment on myanimelist is only about 800th in popularity, so I doubt it’s even a max-money license show. It’s probably one of the 5 or 10 least explicable sequels to be made in the past 10 years. If I ever find out an definitive answer to this question, even if that answer is “passion project funded by the mangaka or the studio”, expect that to be its own article. But right now, there really isn’t one.
Fun With Numbers: Adaptations of Award-Winning Manga and the Myth of Madhouse
It’s fairly frequent among people who have started to get interested in anime enough to start knowing things about the people who make it find themselves encountering the names of certain directors and studios over and over. Kasai Kenichi excels at college life stories. Hiroshi Nagahama was the bold visionary who directed Mushishi. Perhaps one of the more preeminent studios in that regard are Madhouse and Gonzo, the studios behind Death Note and Gankutsou, respectively. They can flash those series names on “from the studio that brought you” title cards of the trailer for anything else they make, despite the fact that Madhouse made the Marvel anime and Gonzo hasn’t been run by the people who made Gankutsuou since 2008. I’m here to make the case for why Madhouse’s reputation, along with a number of others, may be a bit overblown. It’s not that they’re not making awesome anime, but they are picking source material that gives them a lot of help.
This situation with directors can sometimes be a bit like that of the quarterback in American football; they get too much credit when things go well, and too much blame when things go wrong. In reality, lots of factors beyond the men at the top contribute to an anime’s success. I’m here today to take a look at one in particular; the pre-production choice of high-quality of source material. What follows is a look at anime adaptations of Shogakukan/Kodansha Award-Winning manga, including observations based on both their relative frequency over the years, their strength as a function of which studio makes them, and their performance in the marketplace.
Fun With Numbers: Scarce Demand for Simulmanga
This past year, viz media pulled off a first for the non-Japan manga industry. I’m referring to Shonen Jump Alpha, a digital “magazine” offering same-week release of the chapters of some 11 Weekly Shonen Jump manga. It’s pretty cool, and at 26$/year for 48 issues (and a buck per back issue), it’s not a totally unreasonable subscription fee. But that specific business model, one of same-week releases for official translations, is unfortunately not something that’s likely to be transferable to the majority of manga. Especially seinen and josei series with smaller fanbases. If you’ve ever wondered if the manga translation industry will catch up to where the anime industry is now with simulcasts, this article discusses the depressing reality of the situation and why such an outcome is relatively unlikely.
3 Major Anime Industry Sea Changes Explained By Their Effect on TV Anime (Part 3: Blu-Ray Boosting)
Every so often, the anime industry goes through a metamorphosis and comes out on the other side looking a bit different. In parts one and two of this series, I covered how late-night TV timeslots altered the landscape of how adult-oriented anime was produced and how the switch to digital painting affected both the abundance of shows made and the predominant artstyle. Unless you believe that we’re in the middle of the beginning of another one right now with Net-only full-season shows or 3DCG shows,* the most recent major sea change to beset industry was the introduction of Blu-Rays, which came into the field in late 2006 and were making up the majority of sales for most adult-oriented anime by 2009.
3 Major Anime Industry Sea Changes Explained By Their Effect On TV Anime (Part 2: Digital Paint and DVDs)
Welcome to part 2 of this series on how different changes in production and distribution methods affected anime over the years. Last time, I talked about how late-night TV anime came to be the norm for the industry, bringing with it free advertising and the ability to pursue more adult storylines in longer-form media than OVAs (the previously preferred form of adult-oriented anime). The impact of that still plays into today’s topic, though it’s not the subject. This time, the focus is on a pair of subsequent changes that led to still-further increases in production (the second big jump on the graph below).
The first half of the 2000s saw 2 meaningful changes affecting the anime industry. First, studios switched over from old-school cel painting to a digital paint process, reducing production costs and causing a subtle shift in both artstyle and visual presentation. Second, people started buying DVDs over VHS tapes, further reducing production costs (Incidentally DVDs being cheaper to produce than VHS tapes was a key cause of the 2007-2008 WGA strike in America).
3 Major Anime Industry Sea Changes Explained By Their Effect On TV Anime (Part 1: The Late Night Revolution of 1996-1998)
Every so often, the anime industry goes through a period of transition that alters how and for whom anime is made and distributed. Call them paradigm shifts or whatever; I call them sea changes. There are at least 4 major sea changes that I know of that have significantly altered the industry: the OVA boom of the late 80s/early 90s, the transition of TV anime from daytime to late-night from 1996-1998, the transition from cels to digital art in the early 2000s, and the Blu-Ray Era starting sometime between 2006 (when they were officially introduced) and 2009 (when they made up a majority of the market). Each one of these transitions had a unique and lasting impact on the industry. Unfortunately, I lack the knowledge to write with any real authority on the OVA boom. This article is the first in a 3-part series covering the latter 3 sea changes and how they influenced the production of anime over the past two decades.
New Directors: What’s In A Resume?
Aside from perhaps the hair episode of Yami Shibai, the 5-minute preview for Go Nagai’s Robot Girls Z was the most impressive, repeatable five minutes of animation I watched last month. If you haven’t seen it yet, it’s over here. Short version: it’s a 5-minute comedy which, but for the more modern cutesy character designs, could totally have been written by Go Nagai. Its style of humor, featuring excessive violence and heroes doing more damage than the monsters they fight, is what he’s always been all about.
Being that I was excited about the project (this was only the 0th episode), I flew over to ann to check the profiles of the freaks involved. As it turns out, the director, Hiroshi Ikehata, has only ever handled one TV series before (Ring ni Kakero), which isn’t a very good sample size to judge a director on. But he has held the position of episode director numerous times, on all manner of series (from A-Channel to Yuyushiki).
There are no less than 8 new directors making their debut in this Summer 2013 season with similar information about their early careers available.* One of them is Hiroko Utsumi, the director of Free! Others run the quality gamut, from C3-Bu’s Masayoshi Kawajiri to Neptunia’s Masahiro Mukai. And, lest I forget, Shishiou Igarashi made a smashing debut with The Unlimited this winter. It’s definitely possible for first-timers to post veteran-esque performances, but far from guaranteed.
This observation led me to a question; what, if anything, can we glean from a first-time director’s experience in the bullpen? If it that experience is important, what part of it is? Is it better to have worked as an understudy to a great creator on a memorable show, or to build up tons of experience grinding out lots of support roles? To attempt to answer these questions, I pulled up resumes for the 11 directors who first got their hands on a serial anime project in 2012 and combed them over to see if anything in particular was a good indicator of their respective performances. This article outlines a number of the potential performance I examined, some better than others.